A hazard of this procedure
circulation (Browman, Harris, and Armstrong 1977).
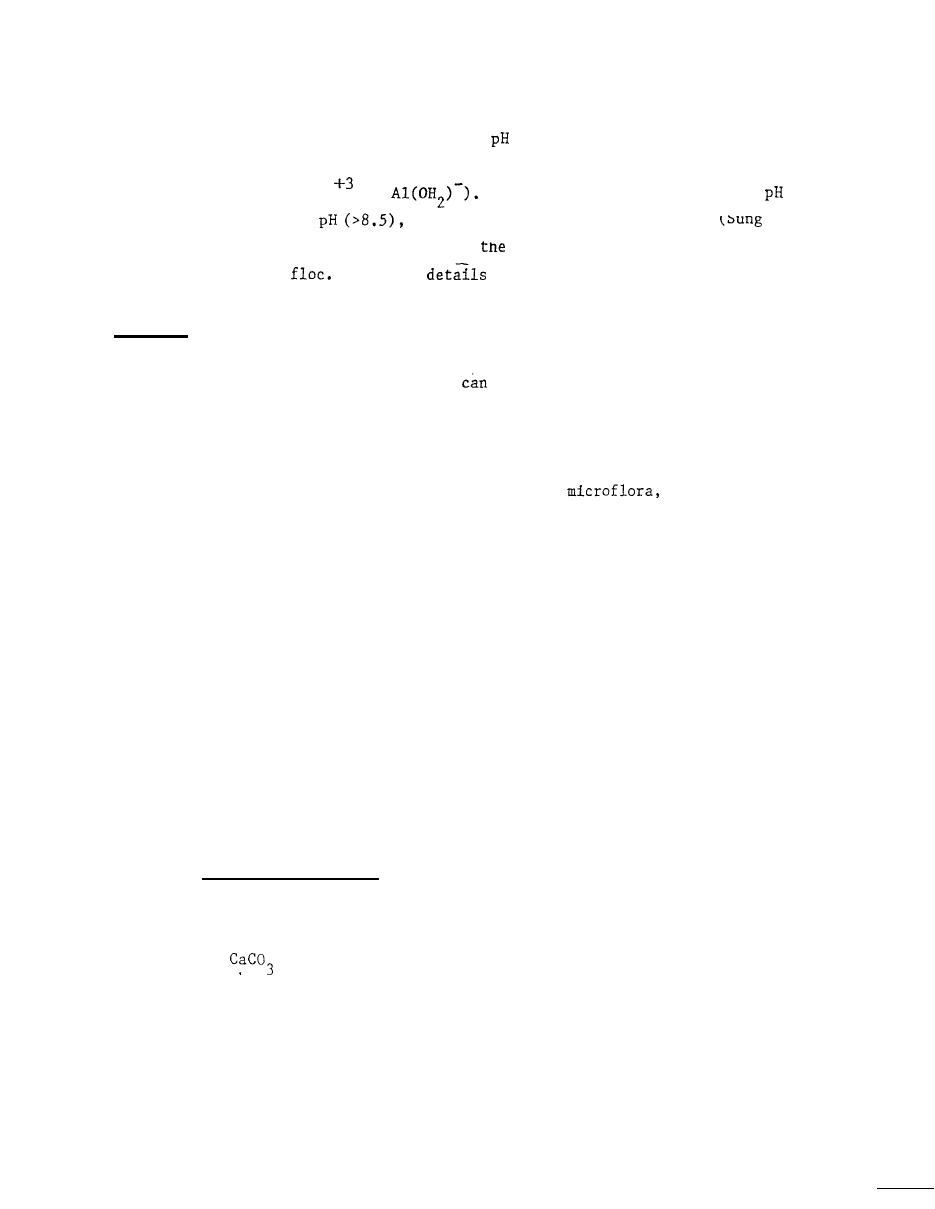
when using alum, depending upon
is the depression of stream or reservoir
buffering capacity, and the subsequent appearance of a potentially toxic dis-
solved aluminum form (Al
If sodium aluminate is used,
will
or
increase, and at high
dissolved aluminum again appears
and
Another hazard involves
smothering of stream invertebrates
Rezania 1984).
Further
of aluminum chemistry are found in
with the deposited
Cooke et al. (1986) and Burrows (1977).
Wetlands
Wetlands, and man-made artificial wetlands or settling basins dominated
intercept significant amounts of
by rooted plants and their epiphytes,
nutrients and suspended solids under certain conditions.
While rooted plants
may absorb a comparatively small amount of nutrients, their presence creates
barriers to water flow and enhances water detention time and thus. contact with
the major storage compartments of a wetland, the
detritus, and
Deposition of suspended materials will also
sediments (Howard-Williams 1985).
be enhanced when water flow-through is impeded by the presence of vegetation.
In many cases, the nutrient retention capacity of a wetland is limited
on a short-term basis to the growing season, and on a long-term basis to the
High initial nutrient removal rates may
saturation of storage compartments.
be followed, in several years, by large nutrient exports. Harvesting of
macrophyte biomass may prolong the wetland as a nutrient sink.
Wetlands with
predominantly mineral soils having a high aluminum content are far better
phosphorus sinks than wetlands with peat soils.
Terrestrial ecosystems, how-
ever, retain far more nutrients than wetlands (Howard-Williams 1985,
Richardson 1985).
Lee, Bentley, and Amundsen (1975) list the following beneficial and
adverse effects of wetlands on the quality of water discharged from them:
Beneficial effects:
Denitrification of nitrate under anaerobic conditions permits
l
methane formation and the degradation of certain organic
compounds.
precipitates, along with other chemicals such as
l
phosphorus.
Sediments are trapped.
l
Nutrients are removed during summer months, especially if flow is
l
diffuse.
35



 Previous Page
Previous Page
