
|
|

|
||
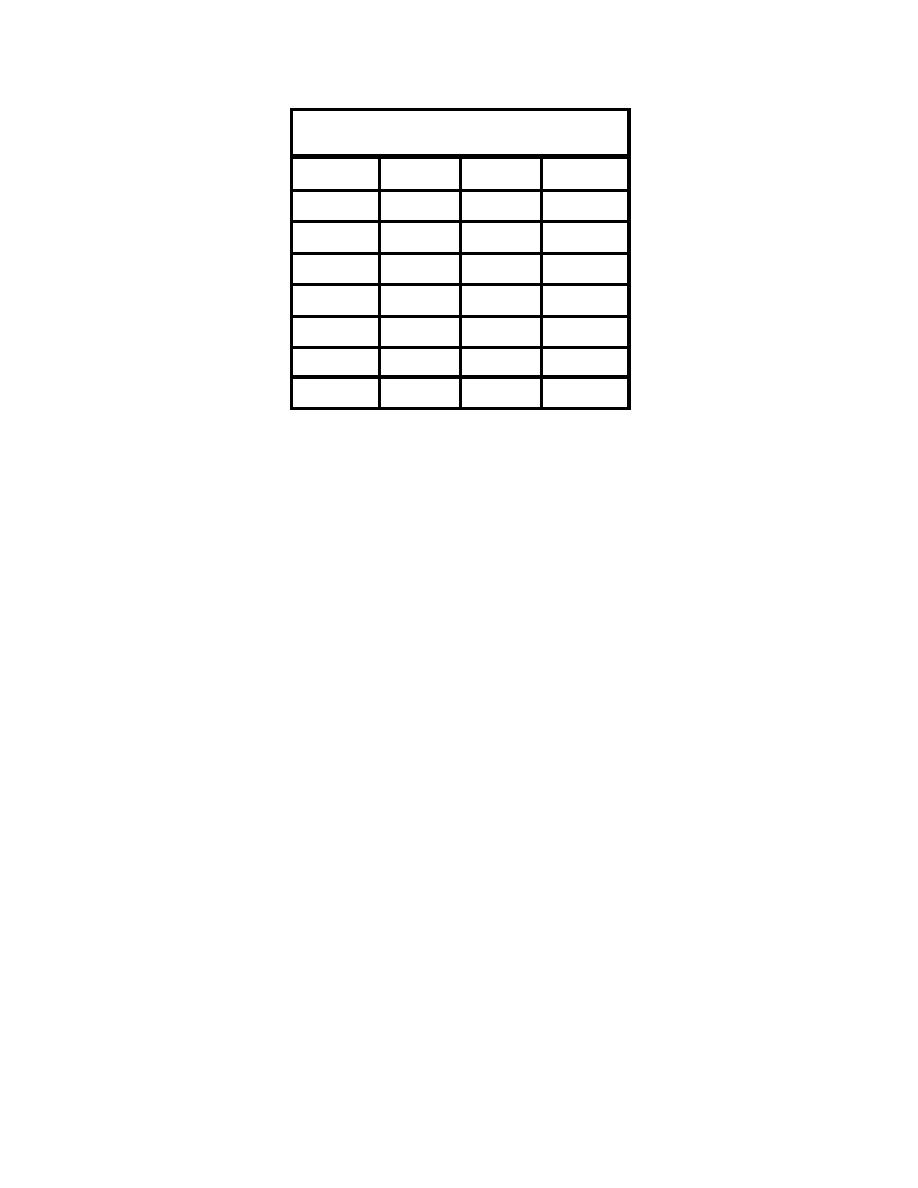 Table 1.1.12 Export Coefficients Compiled from
Literature Reviews by Reckhow and Dodd
Crop
TN
TP
Studies
kg/ha-yr
kg/ha-yr
n
Hay
4.09
0.64
1
Alfalfa
5.6
0.91
5
Cotton
10.2
4.45
2
Tobacco
13.3
4.5
3 and 7
Corn
11.32
2.74
15
Soybeans
26
13
3
1.1.3.4 Construction
Erosion, sedimentation, and hydromodification from construction sites can be an
important cause of water pollution and loss of designated uses in a waterway. Residential construction
without erosion control BMPs can cause a streambed to be filled with sediment. Highway construction
without effective BMPs can fill small lakes with sediment, making them useless for their intended uses.
1.1.4 POINT SOURCES
1.1.4.1 Municipal and Industrial Waste Water
Point sources are, in principle, relatively straightforward to control. Wastewaters originate from
households, industries, and combined sewers. They are collected and transported to the treatment plant
where they are processed. The effluent then flows to streams where it is diluted by streams, lakes, or
estuaries. Occasionally part of the water supply volume for one community is the discharge from the
wastewater treatment plant from the community upstream. Additional methods of disposal include
irrigation, infiltration, evaporation from lagoons, and submarine outfalls extending into the ocean
(Viessman and Hammer, 1985).
Wastewater volume and concentration information by treatment process provides information
for calculating wastewater pollutant loading (Table 1.1.13).
1.1-36
|
||
 |
||